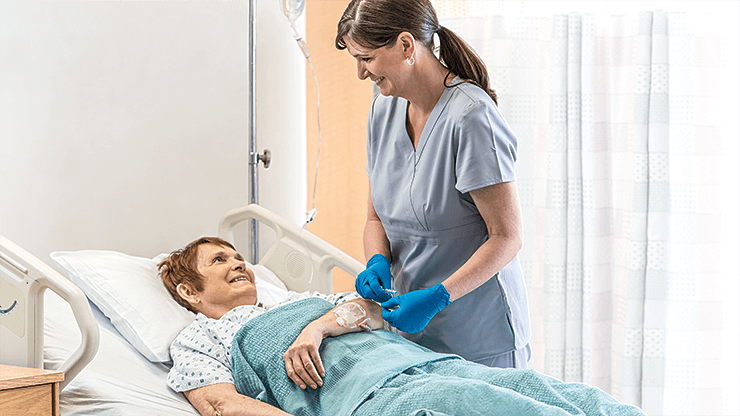
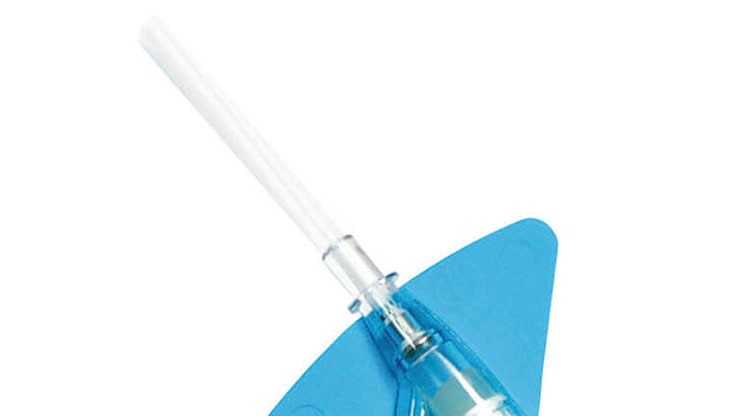
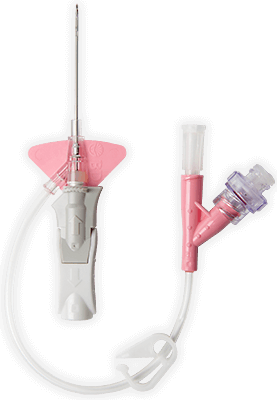
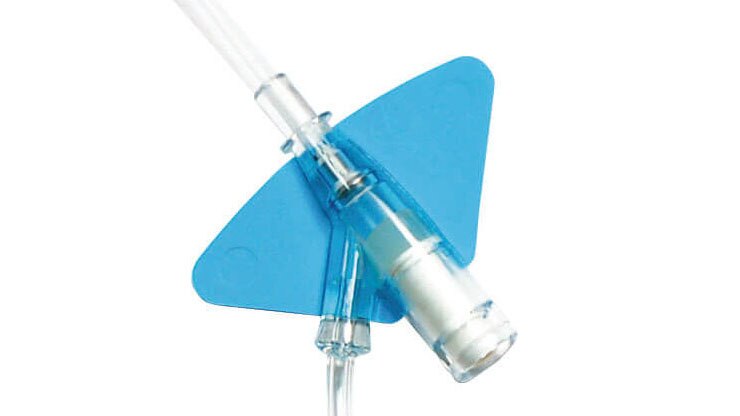
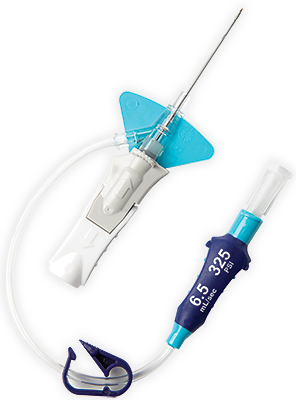
* Rispetto a un sistema aperto
**I risultati e i risparmi possono variare per altre istituzioni.
†Confronto con un catetere FEP.
‡Se usato con una medicazione specificatamente progettata per BDNexiva™ 3M™ Tegaderm™ IV.
§ Rispetto al catetere Introcan Safety® B. Braun con dispositivo di stabilizzazione Bard Statlock® IV Ultra
|| Rispetto a 96 ore in un sistema aperto.
¶Rispetto a un catetere privo di tecnologia Blood Control.
Riferimenti
- González López J, Arribi Vilela A, Fernández Del Palacio E, et al. Indwell times, complications and costs of open vs closed safety peripheral intravenous catheters: a randomized study. J Hosp Infect. 2014;86(2):117-126.
- Bausone-Gazda D, Lefaiver CA, Walters SA. A randomized controlled trial to compare the complications of 2 peripheral intravenous catheter stabilization systems. J Infus Nurs. 2010;33(6):371-384.
- Maki DG, Ringer M. Risk factors for infusion-related phlebitis with small peripheral venous catheters. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114(10):845-854.
- Gorski, L. A., Hadaway, L., Hagle, M. E., Broadhurst, D., Clare, S., kleidon, T., Meyer, B. M., nichel, B., Rowley, S., Sharpe, E., & Alexander, M. 2021, Standard di pratica Infusion Therapy, ottava edizione. Journal of Infusion Nursing. Sezione 6 (S108). https://doi.org/10.1097/nan.0000000000000396
- O’Grady NP, Alexander M, Burns LA, et al. Linee guida per la prevenzione delle infezioni da catetere intravascolare. CDC. 2011:16.
BD-113271 (09/2021)