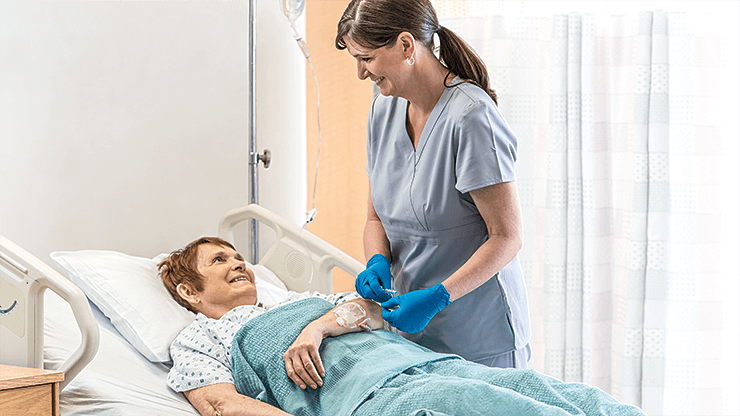
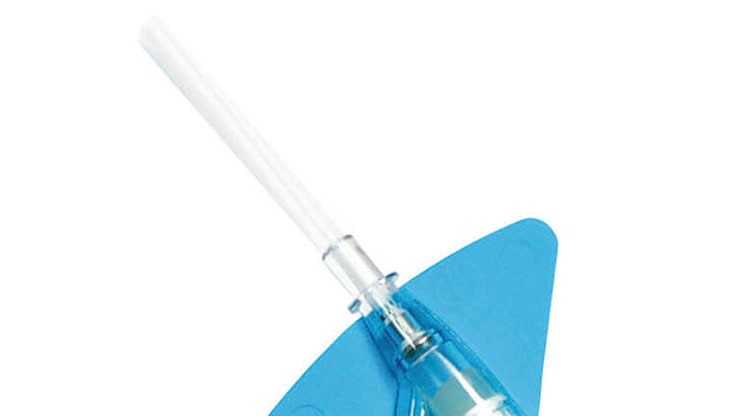
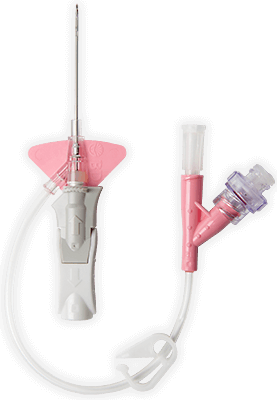
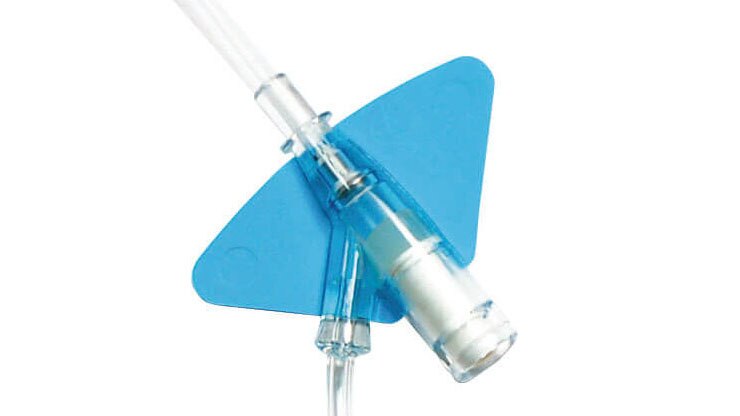
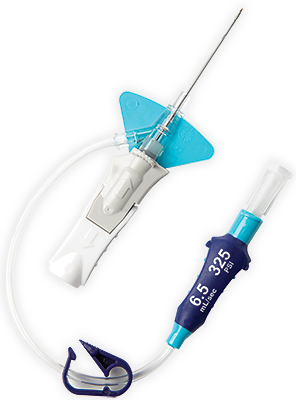
Materiał biologiczny Vialon™ firmy BD
,Zastrzeżony prawnie materiał biologiczny BD Vialon™ zmiękcza się w żyle nawet o 70%, umożliwiając dłuższe utrzymywanie cewnika 3† i zmniejszając ryzyko mechanicznego zapalenia żył nawet o 50%.3†
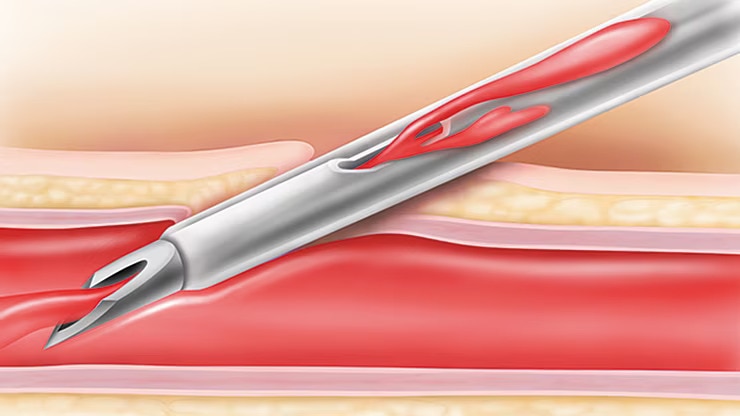
,Technologia igieł Instaflash™ firmy BD
,Zapewnia szybką wizualizację krwi, dzięki czemu może poprawiać skuteczność wprowadzania cewnika do naczynia, a tym samym zmniejszyć liczbę powtórzeń cewnikowania.
,Wbudowana platforma stabilizująca‡
,Redukuje przemieszczenia o 84%2§ i jest zgodna z wytycznymi dotyczącymi stabilizacji cewnika, opracowanymi przez Infusion Nurses Society (INS)4 oraz Centers for Disease Control (CDC).5
,Fabrycznie dołączony przewód przedłużający
,Fabrycznie dołączony przewód przedłużający tworzy obieg zamknięty, minimalizujący ryzyko kontaktu z krwią podczas wprowadzania cewnika* 2 , zgodny ze standardami INS.
,Mniej powikłań
,Zintegrowany przewód przedłużający i platforma stabilizująca‡ mają za zadanie ograniczenie manipulacji i ruchu w miejscu wprowadzenia. Wykazano, że zmniejszają przesunięcia cewnika§ i mechaniczne zapalenie żył nawet o 50%.1,2
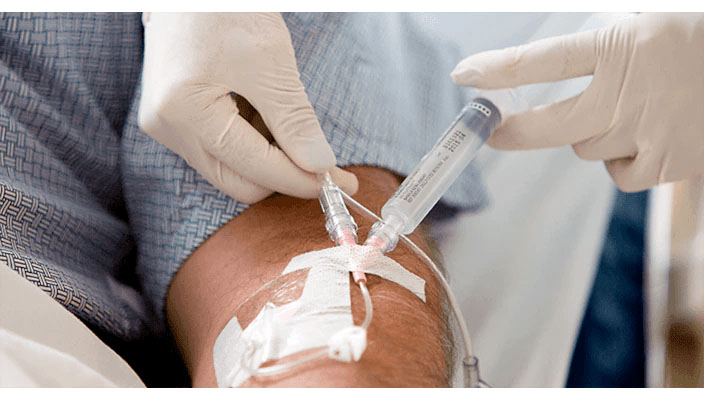
,Mniejsze ryzyko kontaktu z krwią
,Fabrycznie połączone systemy cewnika dożylnego BD Nexiva zmniejszają ryzyko kontaktu z krwią podczas wprowadzania cewnika o 98%.2*
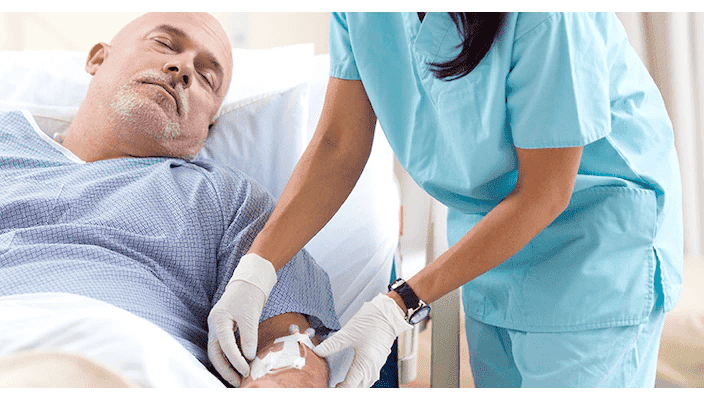
,Cewnik dożylny BD Nexiva może być utrzymywany w naczyniu dłużej
,W randomizowanym badaniu porównującym cewnik dożylny BD Nexiva z cewnikiem działającym w systemie otwartym, średni czas utrzymania cewników dożylnych BD Nexiva wyniósł sześć dni, natomiast w systemie otwartym cztery dni.1
,Cewnik dożylny BD Nexiva utrzymuje miejsca wprowadzenia
,Dzięki dłuższemu utrzymaniu miejsc wprowadzenia cewnik dożylny BD Nexiva pozwala na dostarczanie pacjentom potrzebnych leków zgodnie z planem, potencjalnie skracając czas ich hospitalizacji.1,2
,Może obniżać koszty i zmniejszać opóźnienia w leczeniu
,W badaniu klinicznym z roku 2014 dłuższy czas utrzymania (6 dni)|| cewnika dożylnego BD Nexiva™ przełożył się na obniżenie kosztów leczenia nawet o 786 257,05 EUR rocznie na 1000 łóżek w porównaniu do systemu otwartego.1**
,Większa stabilizacja cewnika
,Stabilizowanie cewnika jest uznawane za interwencję mającą zmniejszyć ryzyko powikłań. Może przynieść korzyści w postaci zapobiegania zakażeniom krwi związanym z cewnikiem (CRBSI).4,5
,Zintegrowana konfiguracja
,Infusion Nurses Society (INS) zaleca ograniczenie stosowania urządzeń dodatkowych, aby ograniczyć konieczność dodatkowych manipulacji oraz zmniejszyć ryzyko zanieczyszczenia i rozłączenia cewnika.4