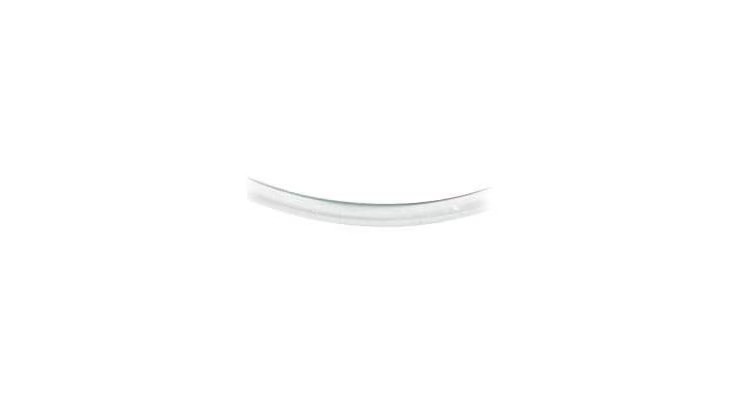
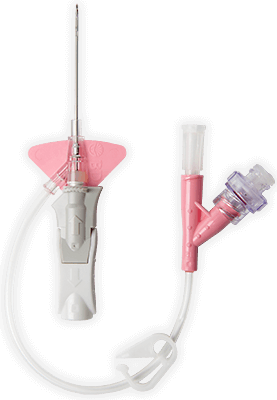
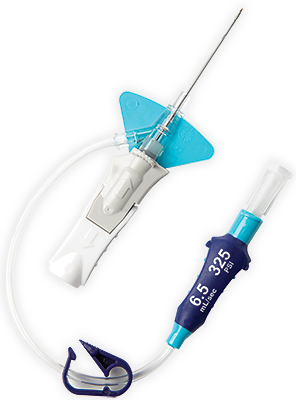
Biomaterial BD Vialon™
,El biomaterial patentado de BD Vialon™ se ablanda hasta un 70 % en la vena, lo que permite tiempos de permanencia más largos3† y reduce la posibilidad de flebitis mecánica hasta un 50 %.3†
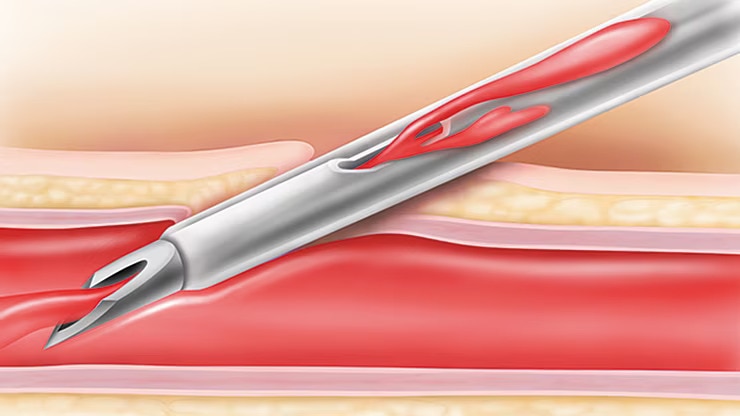
,Tecnología de aguja BD Instaflash™
,Proporciona una visualización rápida de la sangre que puede facilitar la inserción correcta y, por tanto, reducir el número de intentos.
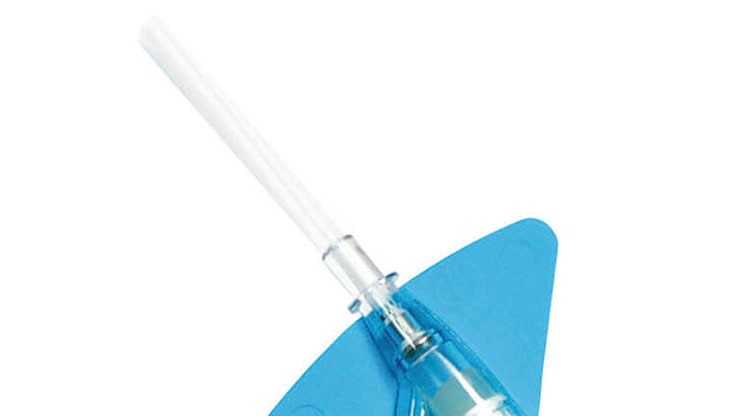
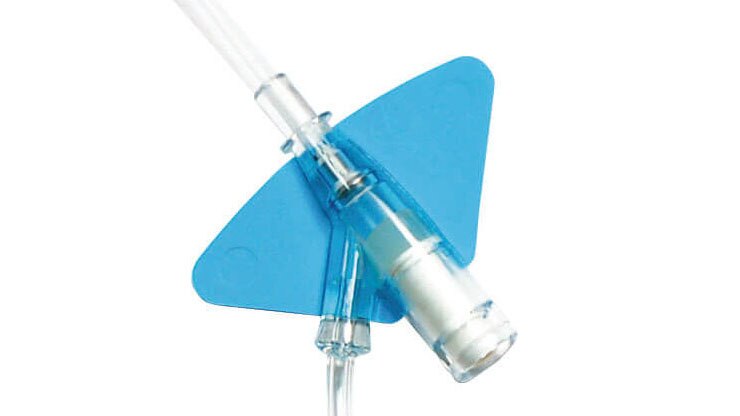
,Plataforma de estabilización incorporada‡
,Reduce el desprendimiento en un 84 %2§ y cumple con las directrices de estabilización de catéteres establecidas por la Sociedad de personal de enfermería competente para practicar infusiones (Infusion Nurses Society, INS)4 y los Centros para el Control y la Prevención de Enfermedades (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC).5
,Alargadera preconectados
,Los tubos de extensión preconectados ofrecen un sistema cerrado para minimizar la exposición a la sangre durante la inserción del catéter*2 y cumplen con las normas de la INS.4
,Reduce las complicaciones
,La plataforma de estabilización y los tubos de extensión integrados‡ están diseñados para reducir la manipulación y el movimiento en el sitio, y se ha demostrado que reducen el desprendimiento2§ y la flebitis hasta un 50 %.1,2
,Disminuye los riesgos de la exposición a la sangre
,Reducción del 98 % de la exposición a la sangre durante la inserción gracias a los sistemas previamente montados del catéter IV BD Nexiva.2*
,Mayor tiempo de permanencia del catéter IV BD Nexiva
,En un estudio aleatorizado en el que se comparó el catéter IV BD Nexiva con un sistema de catéter abierto, el tiempo de permanencia medio de los catéteres IV BD Nexiva fue de seis días, frente a los cuatro días del sistema abierto.1
,El catéter IV BD Nexiva preserva los sitios de inserción
,Al preservar los sitios durante más tiempo, el catéter IV BD Nexiva ayuda a los pacientes a recibir los medicamentos que necesitan según lo programado, lo que podría disminuir la duración de su estancia.1,2
,Pueden ayudar en la reducción de costes y retrasos en el tratamiento
,En un estudio clínico de 2014, el tiempo de permanencia más largo (6 días)|| del catéter IV BD Nexiva™ permitió reducir los costes en aproximadamente 786 257,05 EUR al año por cada 1000 camas, en comparación con un sistema abierto.1**
,Mayor estabilización del catéter
,La estabilización del catéter está reconocida como una intervención que reduce el riesgo de complicaciones y que puede resultar ventajosa a la hora de prevenir las infecciones sanguíneas relacionadas con el uso de catéteres (CRBSI).4,5
,Configuración integrada
,La INS recomienda limitar el uso de dispositivos complementarios para reducir la posibilidad de contaminación, manipulación adicional y desconexión.4